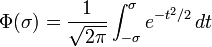




Process fallout quantifies how many defects a process produces and is measured by Defects Per Million Opportunities (DPMO) or PPM. Process yield is, of course, the complement of process fallout (if the process output is approximately normally distributed) and is approximately equal to the area under the probability density function:
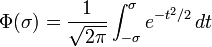
In process improvement efforts, the process capability index or process capability ratio is a statistical measure of process capability: The ability of a process to produce output within specification limits. The mapping from process capability indices, such as Cpk, to measures of process fallout is straightforward:
Short term process fallout:| Sigma level | DPMO | Percent defective | Percentage yield | Cpk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 317,311 | 31.73% | 68.27% | 0.33 |
| 2 | 45,500 | 4.55% | 95.45% | 0.67 |
| 3 | 2,700 | 0.27% | 99.73% | 1.00 |
| 4 | 63 | 0.01% | 99.9937% | 1.33 |
| 5 | 1 | 0.0001% | 99.999943% | 1.67 |
| 6 | 0.002 | 0.0000002% | 99.9999998% | 2.00 |
| 7 | 0.0000026 | 0.00000000026% | 99.99999999974% | 2.33 |
Long term process fallout:
| Sigma level | DPMO | Percent defective | Percentage yield | Cpk* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 691,462 | 69% | 31% | –0.17 |
| 2 | 308,538 | 31% | 69% | 0.17 |
| 3 | 66,807 | 6.7% | 93.3% | 0.5 |
| 4 | 6,210 | 0.62% | 99.38% | 0.83 |
| 5 | 233 | 0.023% | 99.977% | 1.17 |
| 6 | 3.4 | 0.00034% | 99.99966% | 1.5 |
| 7 | 0.019 | 0.0000019% | 99.9999981% | 1.83 |
* Note that long term figures assume process mean will shift by 1.5 sigma toward the side with the critical specification limit, as specified by the Motorola Six Sigma process statistical model. Determining the actual periods for short term and long-term is process and industry dependent, Ideally, log term is where when all trends, seasonality, and all types of special causes had manifested at least once. For the software industry, short term tends to describe operational time frames up to 6 moths, while gradually entering long-term at 18 months.